Weight Sensor: How it Works and how to choose the best one?
What is a weight sensor, what are the different types of sensors and how do they work?
Get to know the functionalities and capabilities of various weight sensors, also known as load cells, in this comprehensive guide.
Weight Sensor manufactured in US by FUTEK Advanced Sensor Technology (FUTEK), a leading manufacturer producing a huge selection of Weight Transducers, utilizing one of the most advanced technologies in the Sensor Industry: Metal foil strain gauge technology. A Weight Transducer is defined as a transducer that converts an input mechanical load, weight, tension, compression or pressure into an electrical output signal (load cell definition). Weight Sensors are also commonly known as Weight Transducer. There are several types of load cells based on size, geometry and capacity.
What is a Weight Sensor?
By definition, a weight sensor is a type of transducer, specifically a weight transducer. It converts an input mechanical force such as load, weight, tension, compression, or pressure into another physical variable, in this case, into an electrical output signal that can be measured, converted and standardized. As the force applied to the sensor increases, the electrical signal changes proportionally.
Weight Transducers became an essential element in many industries from Automotive, High precision manufacturing, Aerospace & Defense, Industrial Automation, Medical & Pharmaceuticals, and Robotics where reliable and high precision measurement is paramount. Most recently, with the advancements in Collaborative Robots (Cobots) and Surgical Robotics, many novel weight measurement applications are emerging.
How does a Weight Sensor work?
Firstly, we need to understand the underlying physics and material science behind the strain weight measurement working principle, which is the strain gauge (sometimes referred to as Strain gage). Metal foil strain gage is a sensor whose electrical resistance varies with applied force. In other words, it converts (or transduces) force, pressure, tension, compression, torque, weight, etc… into a change in electrical resistance, which can then be measured.
Strain gauges are electrical conductors tightly attached to a film in a zigzag shape. When this film is pulled, it — and the conductors — stretches and elongates. When it is pushed, it is contracted and gets shorter. This change in shape causes the resistance in the electrical conductors to also change. The strain applied in the load cell can be determined based on this principle, as strain gauge resistance increases with applied strain and diminishes with contraction.
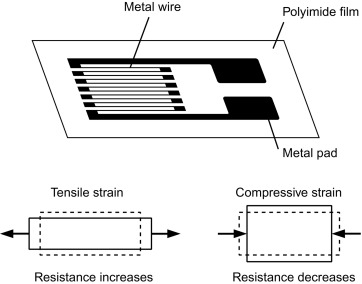
Structurally, a weight transducer is made of a metal body (also called flexure) to which foil strain gauges are bonded. The sensor body is usually made of aluminum or stainless steel, which gives the sensor two important characteristics: (1) provides the sturdiness to withstand high loads and (2) has the elasticity to minimally deform and return to its original shape when the force is removed.
When force (tension or compression) is applied, the metal body acts as a “spring” and is slightly deformed, and unless it is overloaded, it returns to its original shape. As the flexure deforms, the strain gage also changes its shape and consequently its electrical resistance, which creates a differential voltage variation through a Wheatstone Bridge circuit. Thus, the change in voltage is proportional to the physical force applied to the flexure, which can be calculated via the load cell circuit voltage output.
These strain gauges are arranged in what is called a Wheatstone Bridge Circuit (see animated diagram). This means that four strain gages are interconnected as a loop circuit (load cell circuit) and the measuring grid of the force being measured is aligned accordingly.
The strain gauge bridge amplifiers (or strain gauge amplifiers) provide regulated excitation voltage to the load cell circuit and convert the mv/V output signal into another form of signal that is more useful to the user. The signal generated by the strain gage bridge is low strength signal and may not work with other components of the system, such as PLC, data acquisition modules (DAQ), computers, or microprocessors. Thus, load cell signal conditioner functions include excitation voltage, noise filtering or attenuation, signal amplification, and output signal conversion.
Furthermore, the change in the amplifier voltage output is calibrated to be linearly proportional to the Newtonian force applied to the flexure, which can be calculated via the load cell circuit voltage equation.
An important concept regarding weight transducers is sensitivity and accuracy. Weight Sensor accuracy can be defined as the smallest amount of force that can be applied to the sensor body required to cause a linear and repeatable variation in the voltage output. The higher the load cell accuracy, the better, as it can consistently capture very sensible force variations. In applications like high precision factory automation, surgical robotics, aerospace, load cell linearity is paramount in order to accurately feed the PLC or DAQ control system with the accurate measurement. Some of our Universal Pancake Load Cells presents Nonlinearity of ±0.1% (of Rated Output) and Nonrepeatability of ±0.05% RO.
Find out info on basic measurement concepts such as sensor resolution, sensor accuracy, and the differences between resolution versus accuracy, and precision vs resolution.
What are the advantages of strain gage-based weight sensors?
Metal foil strain gauge sensors are the most common technology, given its high accuracy, long term reliability, variety of shapes and sensor geometry and cost-effectiveness when compared to other measurement technologies. Also, strain gage sensors are less affected by temperature variations.
- The highest accuracy which may conform to many standards from Surgical Robotics to Aerospace;
- Robust Construction made of either high strength Stainless steel or Aluminum;
- Maintain high performance at the longest possible work life even at the most rigorous conditions. Some load cell designs can go up to billions of fully reversed cycles (lifespan).
- A plethora of geometries and customized shapes, as well as mounting options for ANY scale ANY-where.
- A full gamut of selections with capacities ranging from 10 grams to 100,000 pounds.
What are the types of strain gage-based weight sensors?
Although there several technologies to measuring force, we will focus on the most common type of load cell: metal foil strain gauge. Within the types of weight sensors, there are a variety of body shapes and geometries, each one catering to distinct applications. Get to know them if you want to buy load cell:
- In-Line Load Cell – Most commonly referred to as in-line weight transducers sensor with male threads. This style of force transducer can be used in both tension and compression loading applications. In-line sensors offer high accuracy and high stiffness with minimal mounting clearance needed. They are great for endurance, and press applications.
- Column Load Cell – FUTEK provides a wide range of Canister Load Cells (also known as Column Load Cell) designed for high capacity compression applications such as CNC Machine Vise Clamping Force Test. These models offer robust construction with a capacity ranging from 2,000 to 30,000 lbs. FUTEK has also developed a miniature Load Cell Canister series for applications where size is a critical factor.
- Load Button – These weight transducers have a single flat, raised surface (aka a button) where the compressive force is applied. What’s impressive about load buttons is their low profile design. As small as they are, they are known for their robustness and are used in fatigue applications.
- S-Beam Load Cell – With other names including Z-Beam or S-Type load transducers, the S-Beam weight transducer is a tension and compression force transducer with female threads for mounting. Sporting high accuracy and a thin beam load cell, compact profile, this sensor type is great for in-line processing and automated control feedback applications.
- Thru-Hole Load Cell – Also known as donut load cell or washer load cell, thru-hole force transducers traditionally have a smooth non-threaded inner diameter used to measure compressive loads that require a rod to pass through its center. One of the primary uses of this sensor type is to measure bolt loading.
- Pancake Load Cells – Pancake, canister-style, or universal load cells have a central threaded hole for measuring loads in either tension or compression. These Weight transducers are used in applications needing high endurance, high fatigue life, or high-capacity in-line measurements. They are also highly resistant to off-axis loading.
- Rod-End Load Cell – This load transducer type offers one male thread and one female thread for mounting. The male and female thread combination is well suited in applications where you need to adapt a sensor into an existing fixture.
How to choose a Weight sensor for your application?
We understand that choosing the right load transducer is a daunting task, as there is no real industry standard on how you go about selecting one. There are also some challenges you may encounter, including finding the compatible amplifier or signal conditioner or requiring a custom product that would increase the product’s delivery time.
To help you select your force sensor, FUTEK developed an easy to follow, 5-Steps guide. Here is a glimpse to help you narrow down your choices. Check out our “Important Considerations in Selecting a weight measurement sensor” complete guide for further information.
- Step 1: Understand your application and what you are measuring. Load sensors are different from pressure sensors or torque sensors and they are designed to measure tension and compression loads.
- Step 2: Define the sensor mounting characteristics and its assembly. Do you have static load or is it a dynamic type? Define the mounting type. How will you be mounting this Force Sensor?
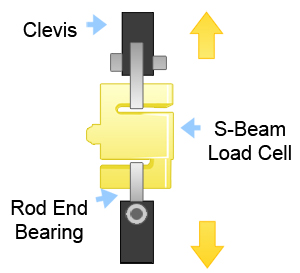
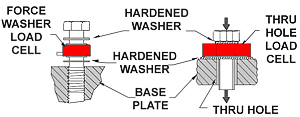
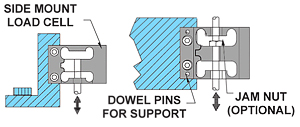
- Step 3: Define your minimum and maximum capacity requirements. Be sure to select the capacity over the maximum operating load and determine all extraneous load (side loads or off-center loads) and moments prior to selecting the capacity.
- Step 4: Define your size and geometry requirements (width, weight, height, length, etc) and mechanical performance requirements (output, nonlinearity, hysteresis, creep, bridge resistance, resolution, frequency response etc.) Other characteristics to consider include submersible (waterproof), cryogenic, high temperature, multiple or redundant bridges, and TEDS IEEE1451.4.
- Step 5: Define the type of output your application requires. Weight transducer circuits outputs voltage in mV/V. So, if your PLC or DAQ requires analog output, digital output or serial communication, you will certainly need a load cell amplifier. Make sure to select the right amplifier as well as calibrate the entire measurement system (load transducer + signal conditioner). This turnkey solution translates into more compatibility and accuracy of the entire weight measurement system.
For more details on our 5-Steps Guide, please visit our “How to choose a Force Measurement Sensor” for complete guidelines.
Why Is It Important to calibrate weight sensors?
Weight Sensor Calibration is an adjustment or set of corrections that are performed on a sensor, or instrument (amplifier), to make sure that the sensor operates as accurately, or error-free, as possible.
Every weight transducer is prone to measurement errors. These structural uncertainties are the simply algebraic difference between the value that is indicated by the sensor output versus the actual value of the measured variable, or known reference weights. Measurement errors can be caused by many factors:
Zero offset (or weight sensor zero balance): An offset means that the sensor output at zero weight (true zero) is higher or lower than the ideal output. Additionally, zero stability relates to the degree to which the transducer maintains its zero balance with all environmental conditions and other variables remaining constant.
Linearity (or non-linearity): Few sensors have a completely linear characteristic curve, meaning that the output sensitivity (slope) changes at a different rate throughout the measurement range. Some are linear enough over the desired range and does not deviate from the straight line (theoretical), but some sensors require more complex calculations to linearize the output. So, weight sensor non-linearity is the maximum deviation of the actual calibration curve from an ideal straight line drawn between the no-pressure and rated pressure outputs, expressed as a percentage of the rated output.
Hysteresis: The maximum difference between transducer output readings for the same applied weight; one reading is obtained by increasing the weight from zero and the other by decreasing the weight from the rated output. It usually measured at half rated output and expressed as a percentage of the rated output. Measurements should be taken as rapidly as possible to minimize creep.
Repeatability (or non-repeatability): The maximum difference between transducer output readings for repeated inputs under identical weight and environmental conditions. It translates into the weight transducer's ability to maintain consistent output when identical weight are repeatedly applied.
Temperature Shift Span and Zero: The change in output and zero balance, respectively, due to a change in transducer temperature.
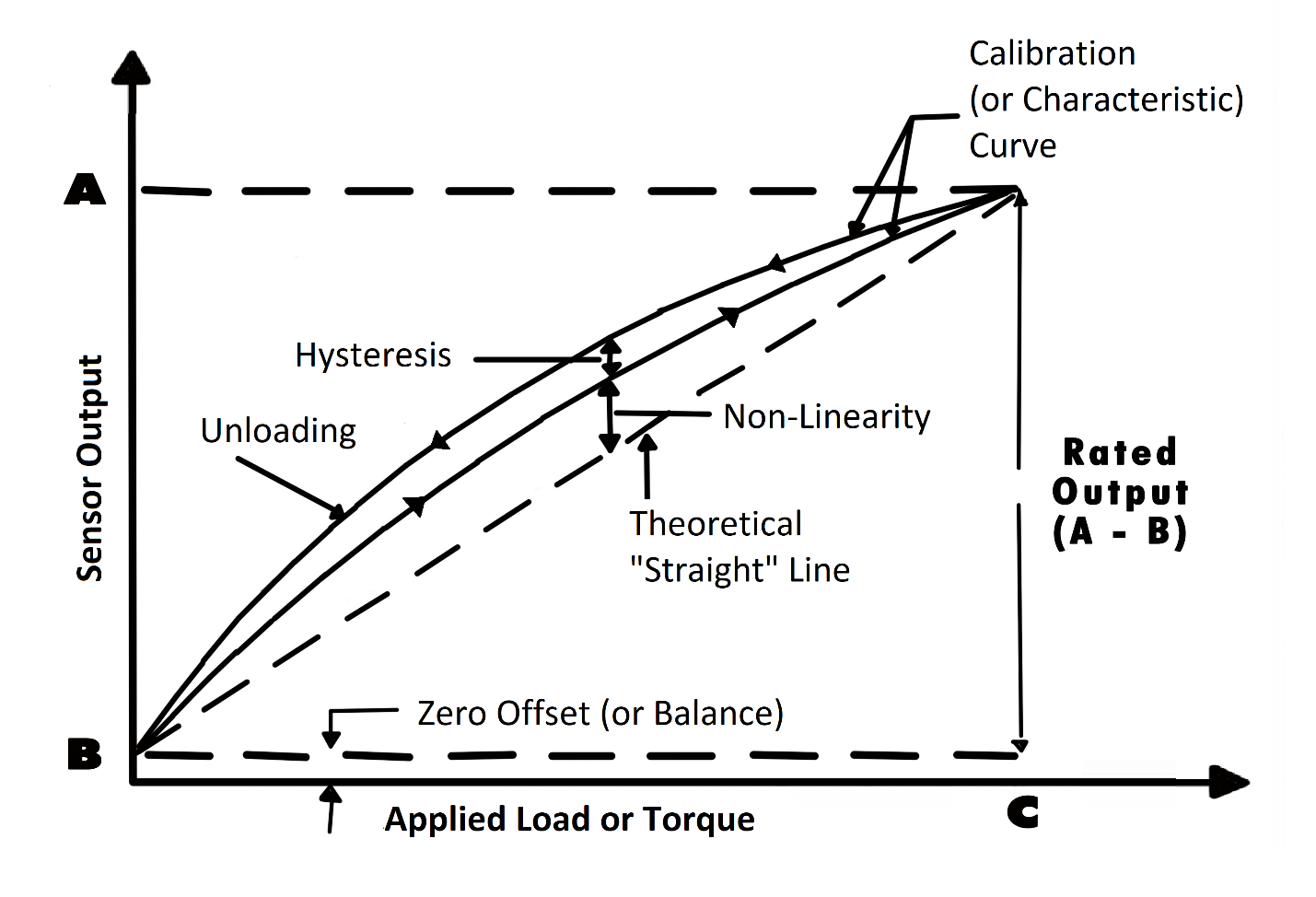
Each weight sensor has a "characteristic curve" or a "calibration curve", which defines the sensor's response to an input. During a regular calibration using the weight transducer calibration machine, we check the sensor's zero offset and linearity by comparing the sensor output under reference weights and adjusting the sensor response to an ideal linear output. The weight sensor calibration equipment also check hysteresis, repeatability and temperature shift when customers request it for some critical weight measurement applications.
For more information about calibration, please refer to our Sensor Calibration FAQ Page.
If you have further questions about calibration terms and definitions, please refer to our Sensor Calibration Terms Glossary.
Want to know what calibration services we offer for your sensor and/or system?
How often should a weight measurement sensor be recalibrated?
As strain gauge weight sensors are exposed to continuous usage, aging, output drift, overload and improper handling, FUTEK highly recommends a yearly recalibration interval. Frequent recalibration helps confirm whether the sensor maintained its accuracy over time and provides a load cell calibration certificate to show that the sensor still meets specifications.
However, when the sensor is used in critical applications and harsh environments, weight sensors may require even more frequent calibrations. Please consult appropriate calibration intervals with our Technical Support team, who will help you evaluate the most economical calibration service interval for your weight transducer.
Check out our Load Cell Store. More than 600+ types of load cells available!
