Besides boosting and optimizing the strain gauge signal in the steps above, signal conditioners/amplifiers also play an important role in mitigating external factors that can affect the sensor output. All sensors, no matter how well-designed and precise they may be, will encounter challenges that affect their performance. Using a high-quality signal conditioner/amplifier minimizes these imperfections and optimizes the sensor’s output. Below are some common challenges that can be mitigated with electronics:
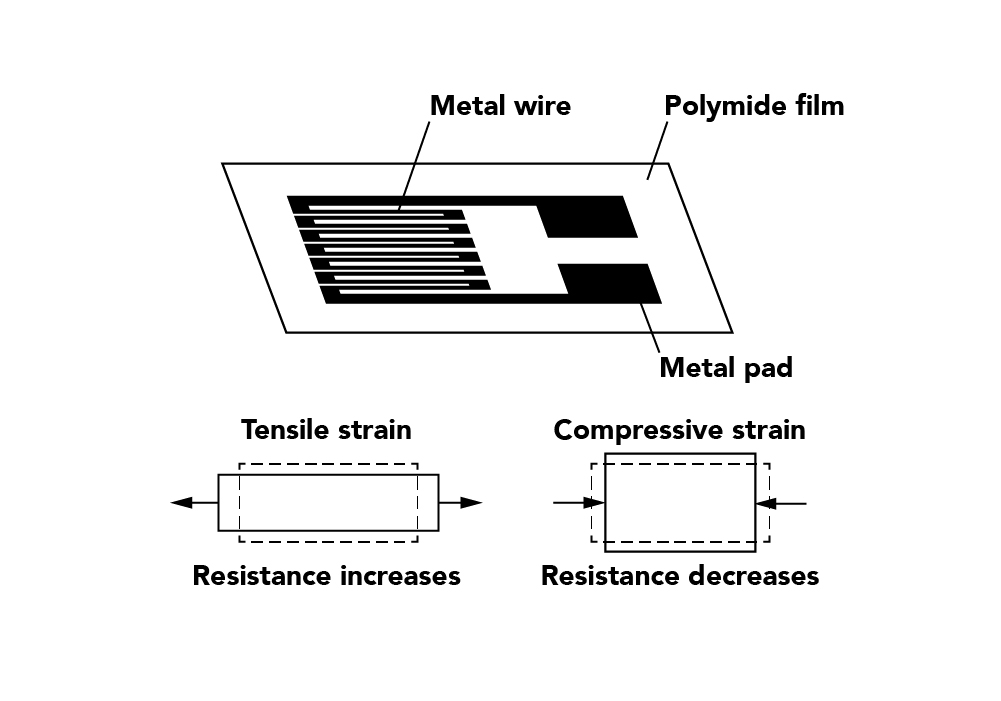
Excitation: Strain gauge-based sensors require an external power supply (excitation) to operate. In other words, the excitation signal is used by the sensor to produce the output signal. As we showed above in our breakdown of the Wheatstone bridge circuit, the output of the bridge is derived directly from the input to the bridge. This means that the quality of the sensor’s output is directly related to the quality of the input (excitation) and that to achieve a clean output, an equally clean input (excitation) must be provided Hence, it’s critical to properly design the excitation circuitry to provide a clean, low drift and well-regulated output and stable excitation signal.
Sensitivity Error: The slope of the characteristic output curve of a sensor usually defines the sensor’s sensitivity. Hence, the amount of deviation from the ideal curve defines the sensitivity error, which could result in the sensor being non-symmetric and also directly impacting the dynamic range (the total range, from minimum to maximum, that could be measured during normal operation). For example, an ideal sensor does not have sensitivity error thus, it is fully symmetrical. However, in practice, the output of a real sensor could deviate up to 20% (sometimes even more) from each direction. In order to minimize the error, this deviation needs to be addressed by the electronics connected to the sensor.
Precision: The degree of reproducibility of a measurement is defined as precision. This means that an ideal sensor would be able to measure the same exact value over and over with the same stimuli. In practice, the output of a real sensor could be impacted by external factors that we cannot fully control, such as the nature of the material that the sensors are made from, or some processes that the sensors need to go through during manufacturing. This shows the importance of keeping the errors introduced by the electronics being at least one order of magnitude lower than errors introduced by the sensor. At FUTEK, we have invested a lot of time investigating and analyzing our manufacturing process to identify these errors, finding a solution for every step in the process, and addressing them in our electronics design process as well. The same concept is valid for the accuracy characteristic of the sensor.
Sensor Resolution: The definition of resolution can be expressed as the smallest detectable change of the input that can be presented in the output. It means that the electronics must be designed to have a higher level of precision that is capable of resolving the output of the sensor to provide a precise measurement.
Offset Error: As we have already established, there is no perfect or ideal sensor, which means that some errors are expected for the sensor output. In other words, the offset error of a sensor is defined as the output that exists when there is no load. FUTEK minimizes the offset error of the sensors during the manufacturing process, but this error cannot be eliminated 100%, which is why electronics are needed to limit its effects.
Linearity Error: The linearity of the sensor could be identified as how much the actual measured output curve of a sensor could deviate from its ideal straight-line curve. Amplifier/signal conditioners will also have some linearity errors, so it is important to consider designing a circuit that provides extremely low error in comparison to the sensor error. This makes sure that the overall system non-linearity remains close to the sensor error. It should be mentioned that in some extreme cases, the electronics are designed to provide linearization. This approach usually involves a lot of complications, such as additional digital/firmware development and enhanced calibration that need to be implemented on the electronics side by understanding the unique nonlinearity characteristic error of every sensor.
There are other factors related to the sensor specs that electronics can help mitigate, such as Hysteresis, Response Time, Bridge Resistance, Sensor Drift, etc. To learn more about these terms, please see FUTEK’s glossary.