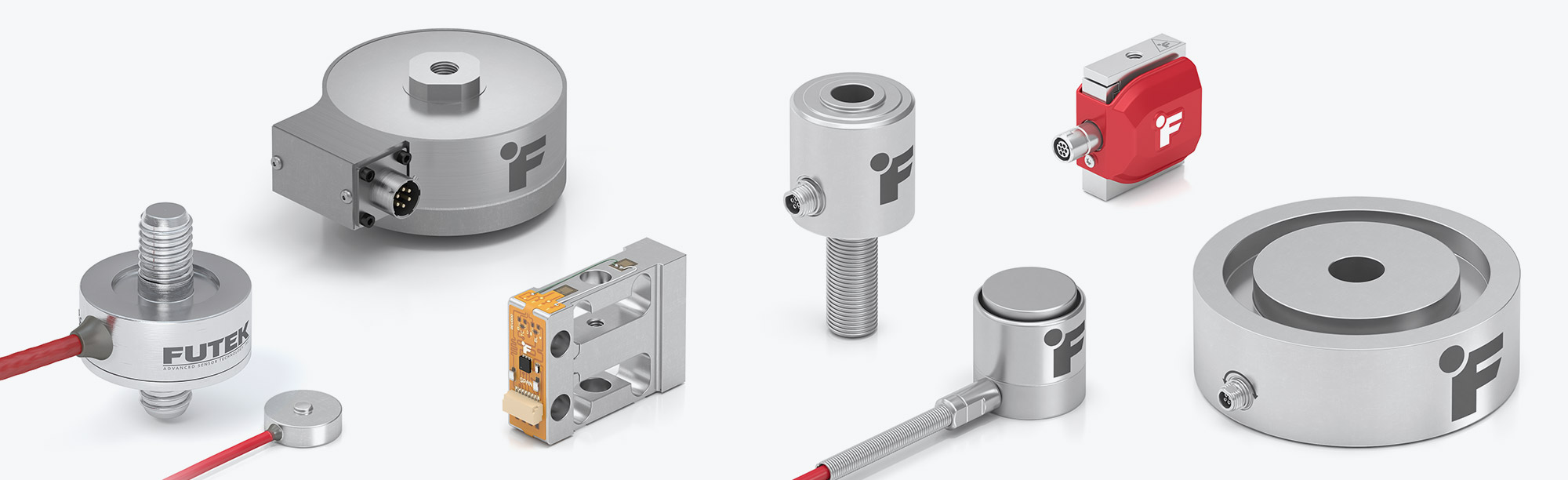
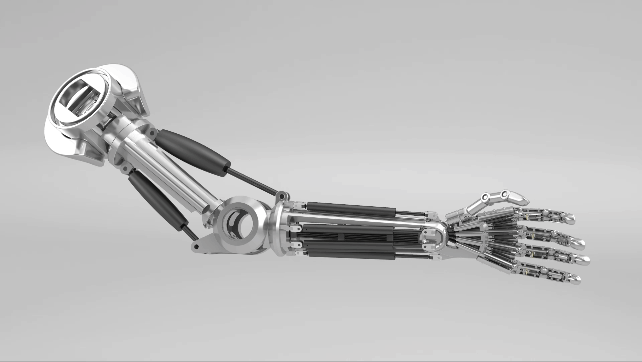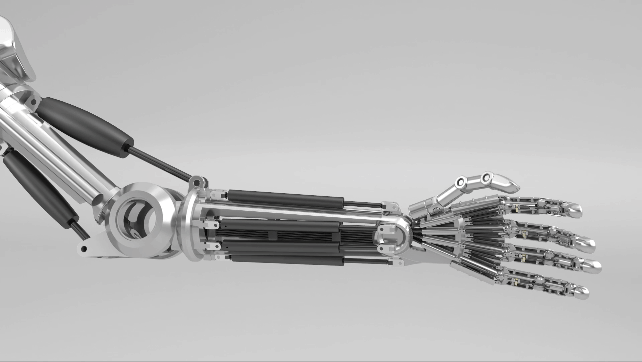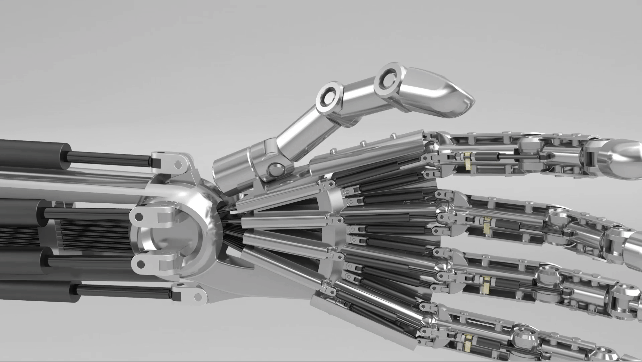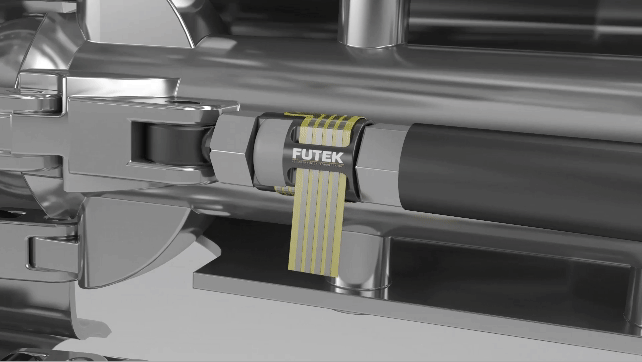
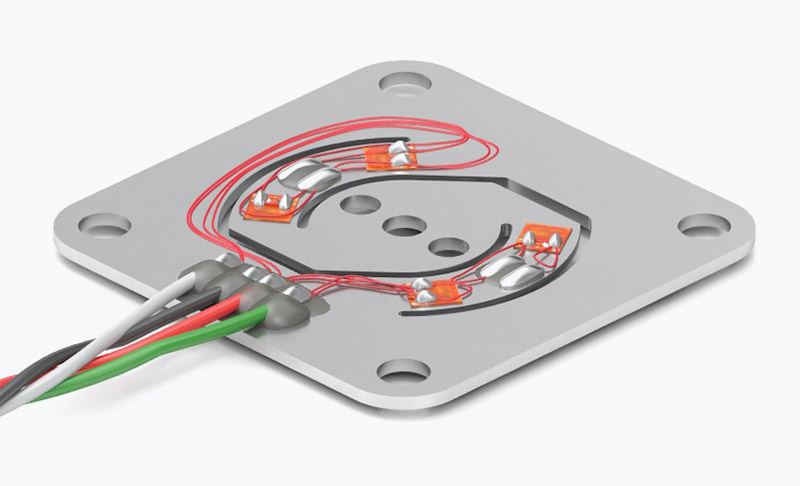
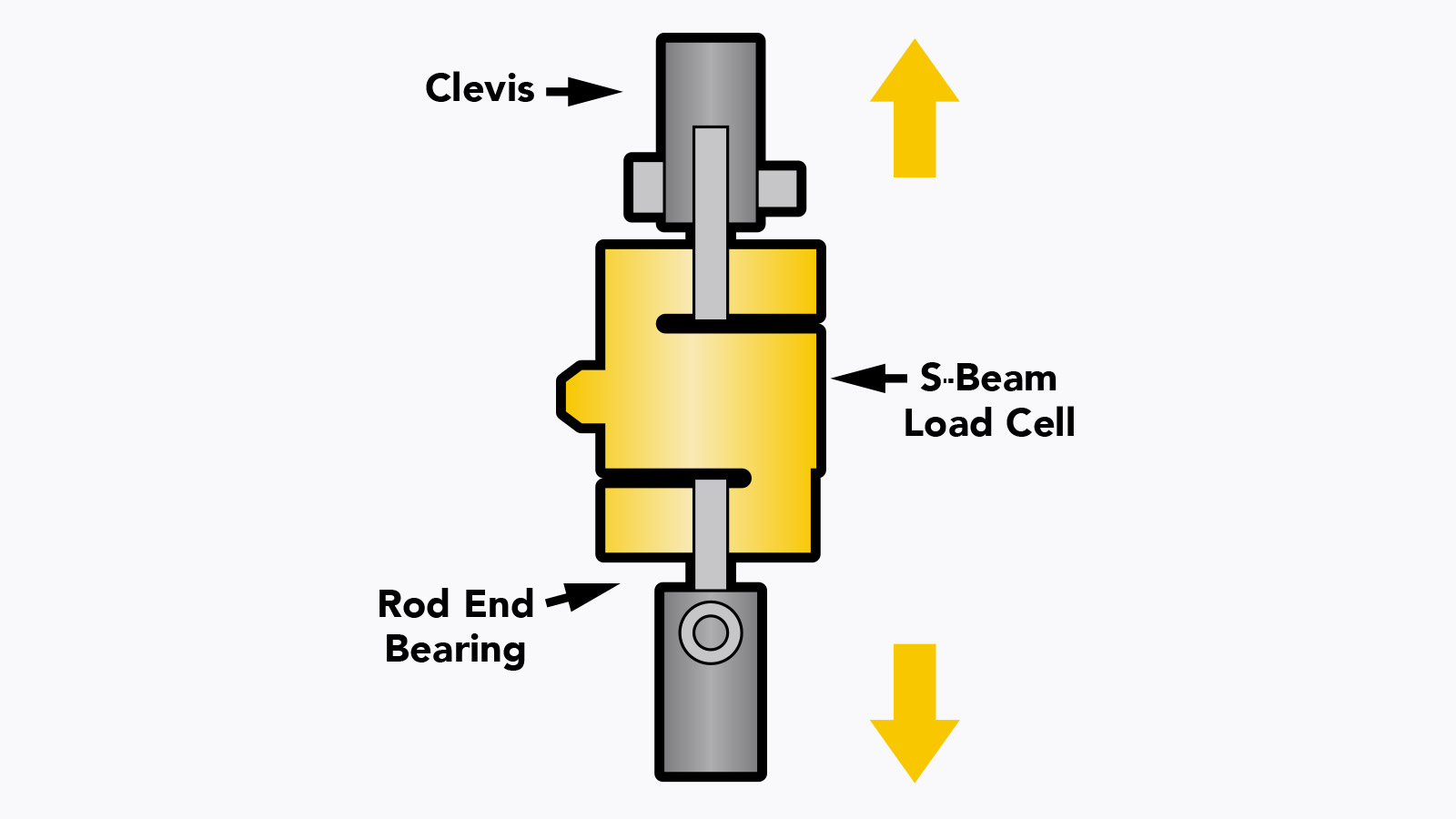
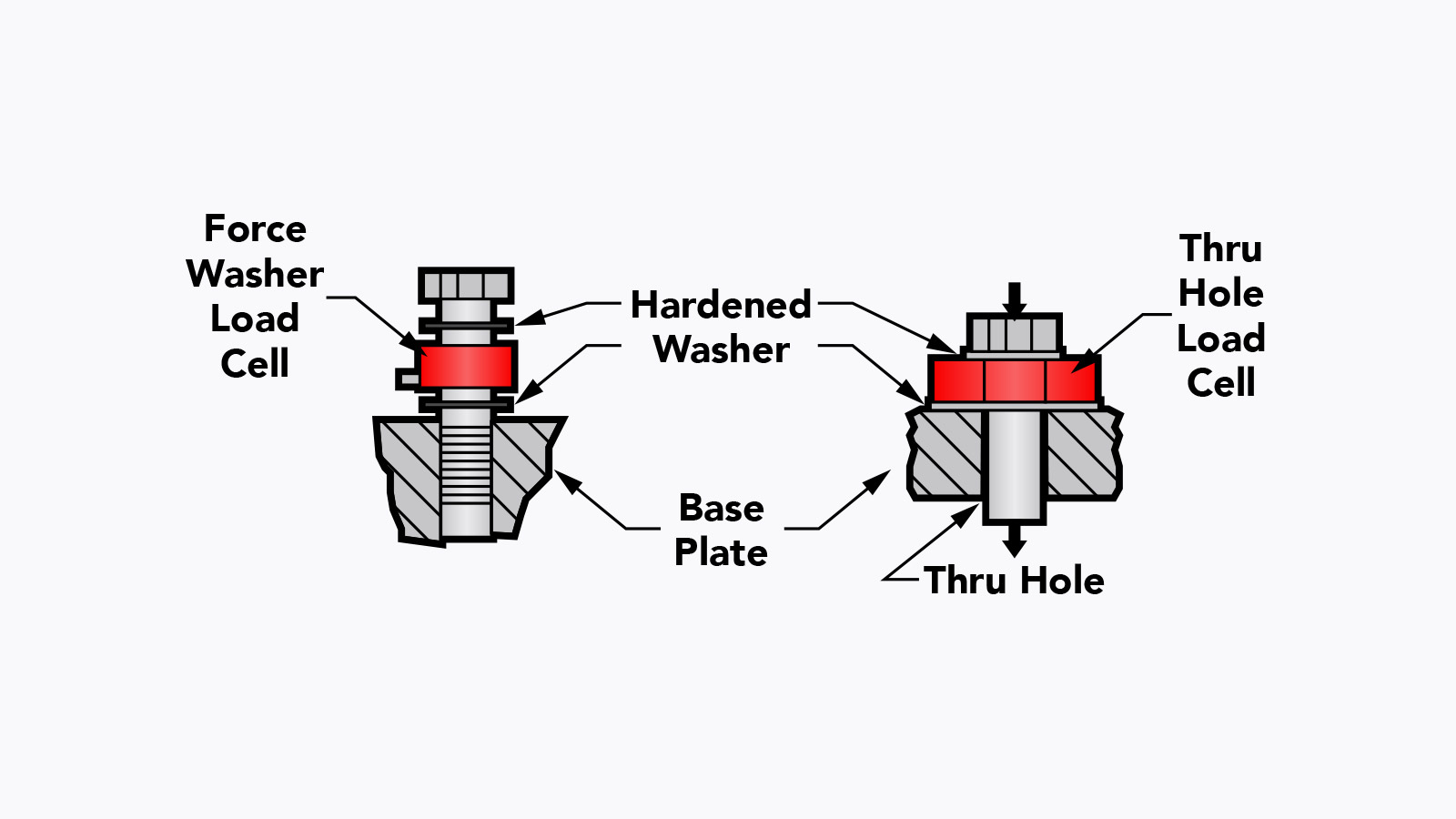
Calibration is an adjustment or set of corrections that is performed on a load cell (force sensor) to ensure that it operates as accurately, or error-free, as possible. Unless it’s properly calibrated, every load cell/force transducer is prone to measurement errors — even the most precise force measurement solution can produce erroneous data. These measurement errors are simply structural uncertainties caused by the algebraic difference between the value that’s indicated by the sensor output versus the actual value of the measured variable, or known reference forces.
What errors does calibration correct?
Measurement errors can be caused many factors, such as the following:
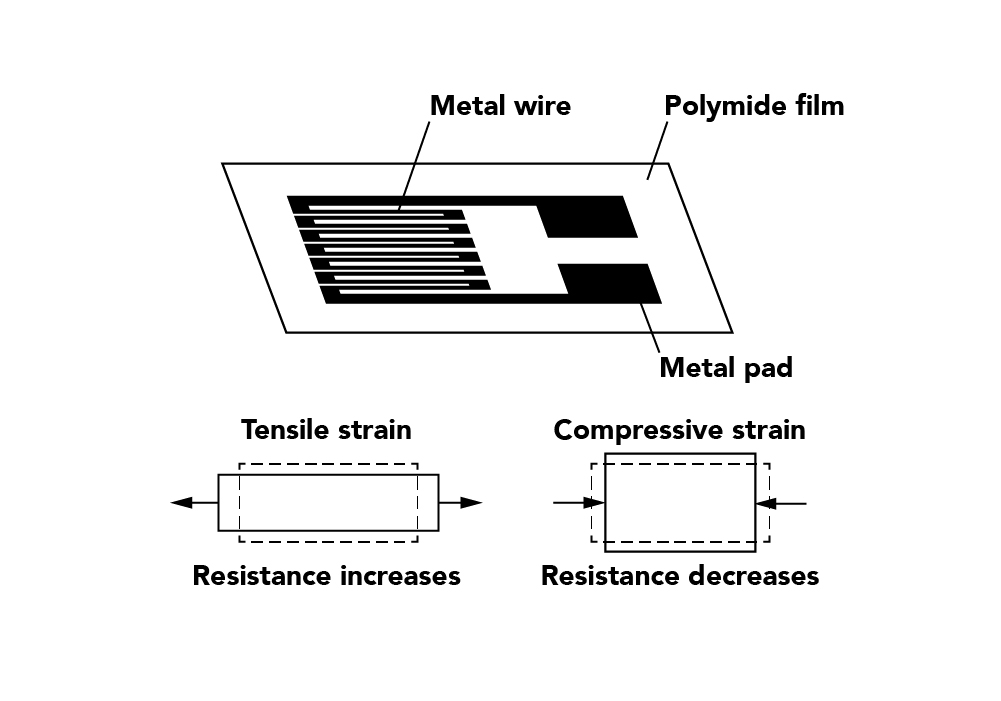
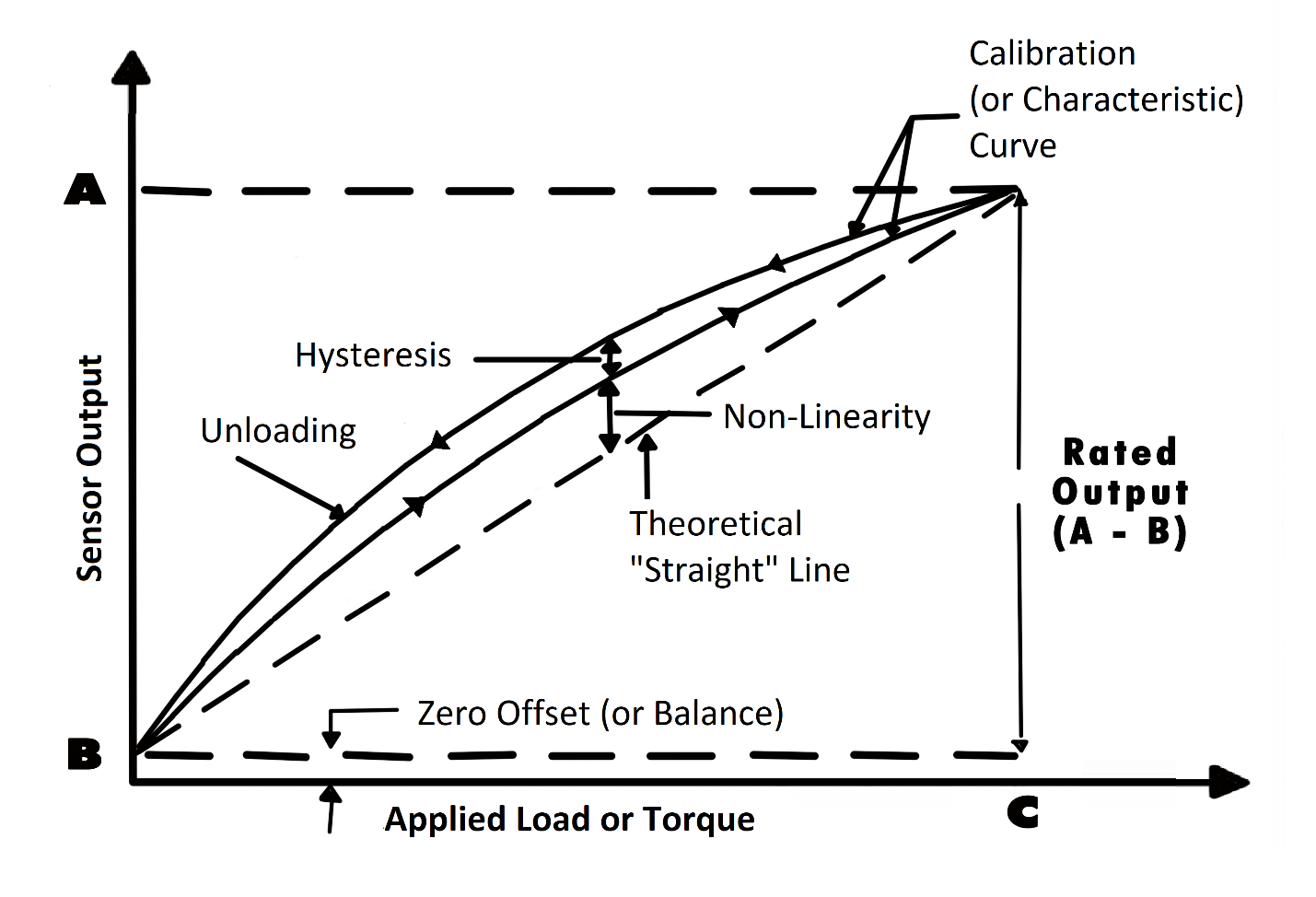
Zero offset (or force sensor zero balance): An offset means that the sensor output at zero force (true zero) is higher or lower than the ideal output. Additionally, zero stability relates to the degree to which the transducer maintains its zero balance with all environmental conditions and other variables remaining constant.
Linearity (or non-linearity): Few sensors have a completely linear characteristic curve, meaning that the output sensitivity (slope) changes at a different rate throughout the measurement range. Some are linear enough over the desired range and do not deviate, but some sensors require more complex calculations to linearize the output. So, force sensor non-linearity is the maximum deviation of the actual calibration curve from an ideal straight line drawn between the no-force and rated force outputs, expressed as a percentage of the rated output.
Hysteresis: Hysteresis is the dynamic lag between an input and an output. You detect it by measuring the maximum difference between output readings for the same applied force; one reading is obtained by increasing the force from zero and the other by decreasing the force from the rated output. It’s usually measured at half-rated output and expressed as a percentage of the rated output. Measurements should be taken as rapidly as possible to minimize creep.
Repeatability (or non-repeatability): The maximum difference between transducer output readings for repeated inputs under identical force and environmental conditions. It translates into the load cell/force transducer’s ability to maintain consistent output when identical forces are repeatedly applied.
Temperature Shift Span and Zero: The change in output and zero balance, respectively, due to a change in load cell/force transducer temperature.
How does calibration correct these errors?
Each force sensor has a “characteristic curve” or a “calibration curve”, which defines the sensor’s response to an input. During a regular calibration using the load cell calibration machine, we check the sensor’s zero offset and linearity by comparing the sensor output under reference weights and adjusting the sensor response to an ideal linear output. The load cell/ force sensor calibration equipment also checks hysteresis, repeatability, and temperature shifts. FUTEK has developed and designed several advanced calibration methods that offer a fully independent offset and span calibration with a precision of 200µV out of 10V.